Acoustic Signal Localization
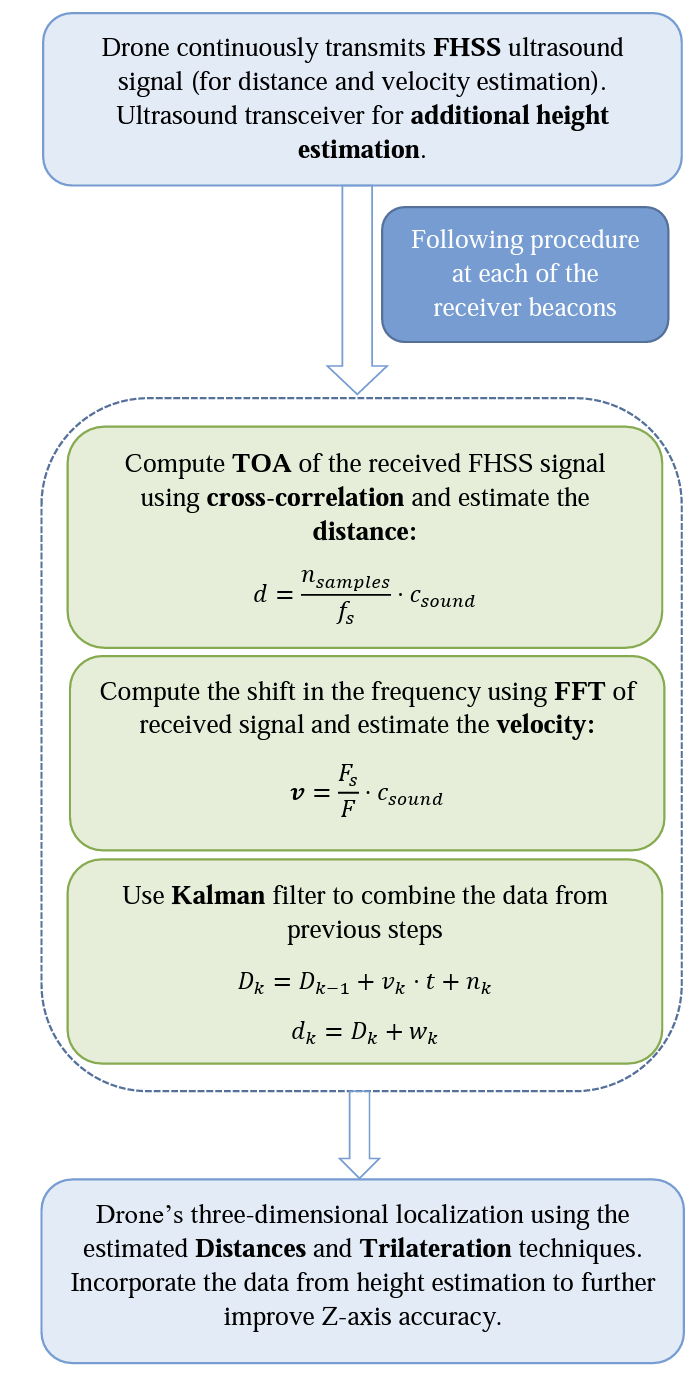
In many scenarios, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), aka drones, need to have the capability of autonomous flight to carry out their missions successfully. In order to fly autonomously, drones need to know their location constantly. Then, based on their current position and the final destination, navigation commands will be generated and drones will be guided to their destination. Localization can be easily carried out in outdoor environments using GPS signals and drone inertial measurement units (IMUs). However, such an approach is not feasible in indoor environments or GPS-denied areas. In this paper, we propose a localization scheme for drones called PILOT (High-Precision Indoor localization for Autonomous Drones), which is specifically designed for indoor environments. PILOT relies on ultrasonic acoustic signals to estimate the target drone’s location. To obtain a precise final estimation of the drone’s location, PILOT deploys a three-stage localization scheme. The first two stages provide robustness against the multi-path fading effect of indoor environments and mitigate the ranging error. Then, in the third stage, PILOT deploys a simple yet effective technique to reduce the localization error induced by the relative geometry between transmitters and receivers, which significantly reduces the height estimation error. The performance of PILOT was assessed in different scenarios, and the results indicate that it achieves centimeter-level accuracy for three-dimensional drone localization.
